

The toilet on the ISS, or 'orbital outhouse' as it is jokingly called by astronauts, is located in the Tranquility module.
Unlike a terrestrial toilet, the ISS toilet has two separate receptacles for solid and liquid waste.
For urine, the astronauts use a hose with a funnel on the front to catch the liquid before it escapes into the rest of the station.
And for solid waste, there is a small hole with a lid which uses fan-powered suction to help everything end up where it needs to go.
However, astronauts have reported that this set-up takes some practice to use and the process can reportedly become somewhat messy.
The ISS can be quite loud as the station's life support systems whirr through the night and the station is regularly bathed in the intense light from the sun as it orbits.
For this reason, eye masks and earplugs are standard issue for astronauts looking to get some much-needed rest.
One of the biggest risks of sleeping in space is not a bad night's rest but the build-up of CO2.
Without gravity, CO2 from the astronaut's breath can form a 'bubble' around their head, potentially suffocating them in their sleep.
Thankfully, the NASA sleeping pods are well-ventilated so that the astronauts can breathe fresh air all night.
NASA assigns its astronauts eight hours of sleep time after a 16-hour working day, but most astronauts generally get about six hours of shut-eye after spending some of their time resting and relaxing.
Forget showering!
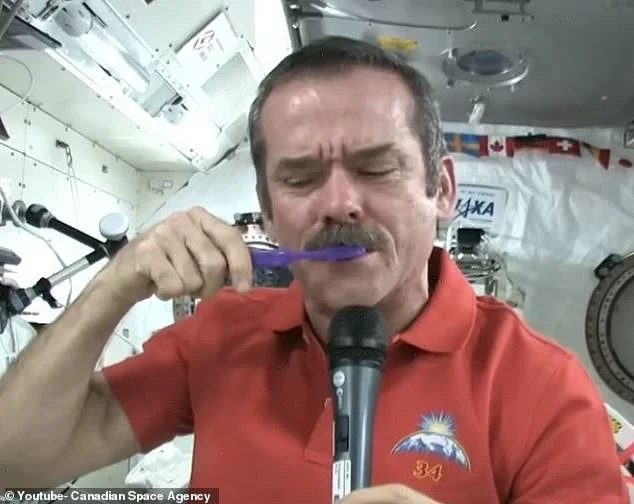
Astronauts on the ISS start their day by brushing their teeth and having a wash.
But as with everything in space, this is far more complicated than it would be on Earth.
Without gravity, water's surface tension causes it to act like a sticky mass, forming large floating orbs that attach themselves to nearby surfaces.

This rules out the possibility of having a shower, so astronauts bathe twice a day using washcloths, with one used for washing and the other for rinsing.
Hair is kept clean using rinseless shampoo and astronauts even give each other haircuts by using a vacuum to suck away the freshly cut hair.
When it comes to brushing your teeth, this is actually quite easy since water sticks to the toothbrush in microgravity.
Since floating wastewater would be a danger to the electronics, astronauts either spit their toothpaste into a piece of paper or just swallow it.


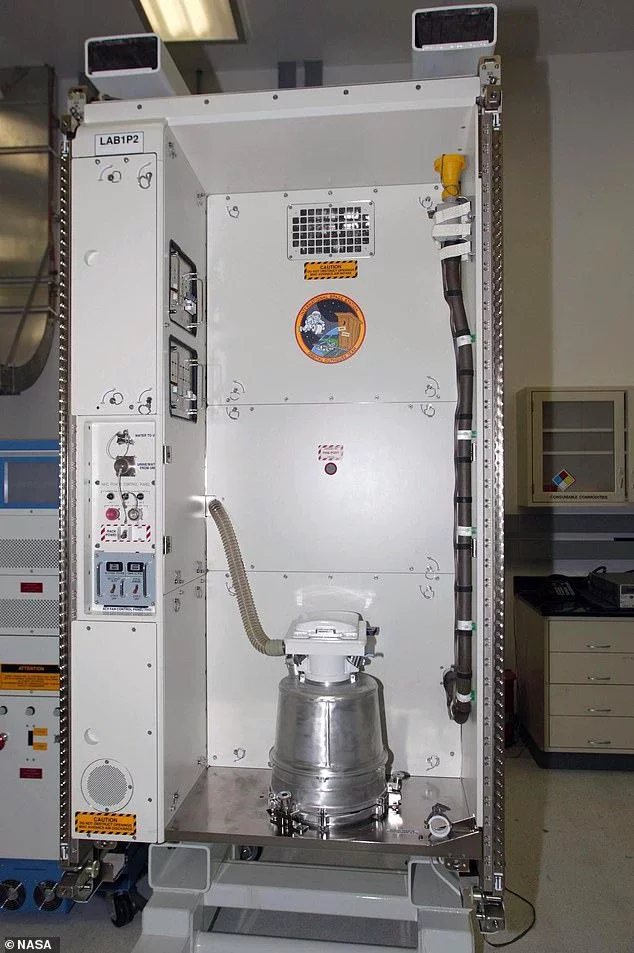
Vacuum-powered toilets
Perhaps the biggest question on everyone's mind is how astronauts are able to go to the toilet while in space.
The toilet on the ISS, or 'orbital outhouse' as it is jokingly called by astronauts, is located in the Tranquility module.
Unlike a terrestrial toilet, the ISS toilet has two separate receptacles for solid and liquid waste.
For urine, the astronauts use a hose with a funnel on the front to catch the liquid before it escapes into the rest of the station.
And for solid waste, there is a small hole with a lid which uses fan-powered suction to help everything end up where it needs to go.

However, astronauts have reported that this set-up takes some practice to use and the process can reportedly become somewhat messy.
In an earlier tour of the ISS, Suni Williams pointed out the various gloves, wet wipes, and disinfectant supplies kept in the toilet to make sure everything remains hygienic.
Once the astronauts have done their business, faeces is sucked into rubbish bags where it is dehydrated and compressed.
These bags are sometimes returned to Earth for study but are usually burned up in the atmosphere.
Urine, meanwhile, is sent through the station's Water Recovery System and transformed back into usable water.
16-hour work days
Most of an astronaut's day aboard the ISS is spent working, and shifts usually last 16 hours with a few breaks for meals.
Work may involve carrying out routine maintenance of the space station and making repairs to the various systems.
In some cases, that could involve 'extra-vehicular activity', otherwise known as spacewalks, in which the astronauts step outside the station.
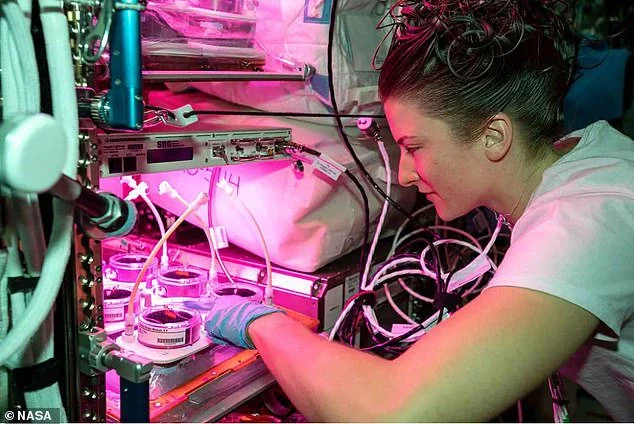
A large part of their work is scientific, with astronauts carrying out various experiments to learn more about the effects of space radiation and microgravity.

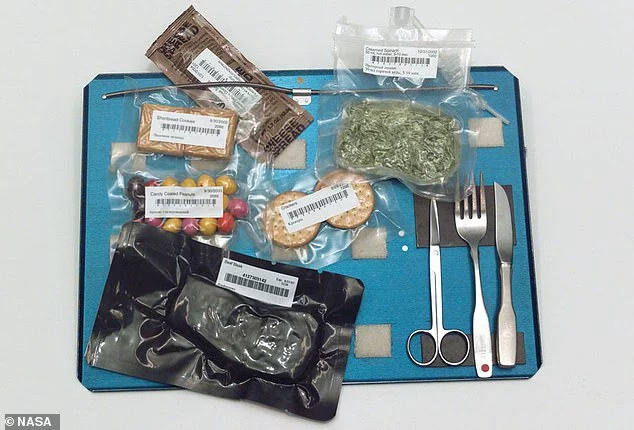
Dehydrated meals (and absolutely no booze)
In the highly demanding environment of space, astronauts need to eat a lot of nutritious food to stay healthy.
That means getting three square meals a day plus snacks to make up a diet of at least 2,500 calories.
Since resupplies are infrequent and fresh produce is heavier to transport, the majority of astronauts' food is dehydrated for long-term storage.
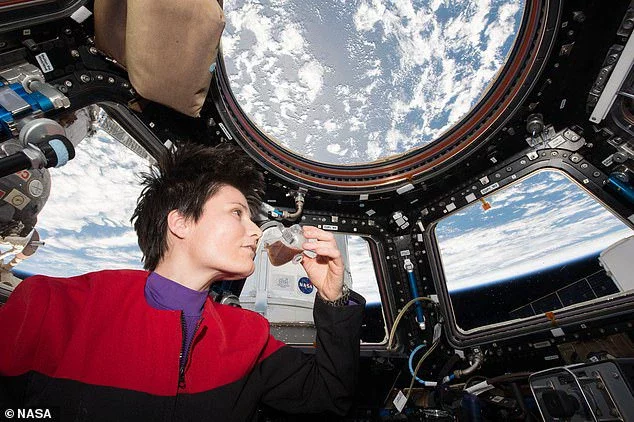
Astronauts use a water gun to rehydrate the packaged food, before heating it in a microwave.
Astronauts are also provided with powdered drinks that can be rehydrated and drunk through a straw.
However, between 2015 and 2017 astronauts also had access to the ISSpresso which was the first ever espresso coffee machine designed for space.
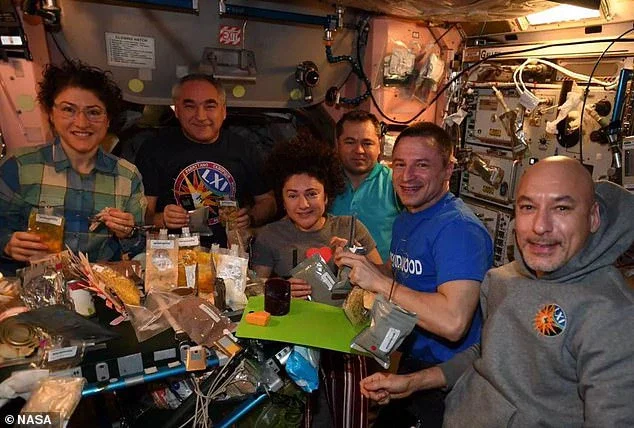

Astronauts eat their meals in the Unity module which is fitted with all the necessary food preparation equipment as well as antibacterial materials on the walls.
Due to their busy schedules, the crew won't often eat together during the week with the exception of Sunday when the team will come together for a group meal.
To maintain some sense of normalcy, the astronauts eat at a table, strapping their legs to chairs and using magnetic trays to hold their food in place.
The biggest difference in an astronaut's diet is that booze is absolutely off the cards.
NASA has forbidden drinking alcohol on any mission on the grounds that astronauts need to be alert and healthy at all times.
To this day, Buzz Aldrin remains the only person to have consumed alcohol in space after he drank a small amount of wine during a secret communion service in the moon lander.

At least two hours of exercise a day
In addition to eating well, astronauts need a lot of exercise to remain fit and healthy.
NASA astronauts are required to do two hours of exercise every day while on the ISS and are carefully monitored for fitness and health.
Without the need to fight against gravity, astronauts' muscles can quickly shrink, leading to potential health complications.
This is part of the reason that many astronauts are unable to walk for a time after re-entering Earth's gravity.
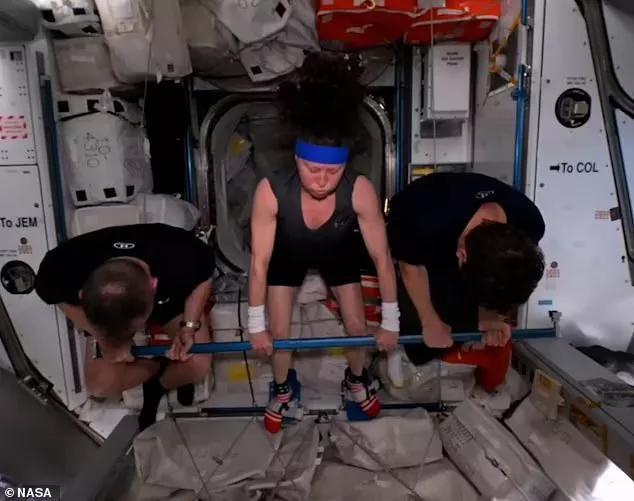
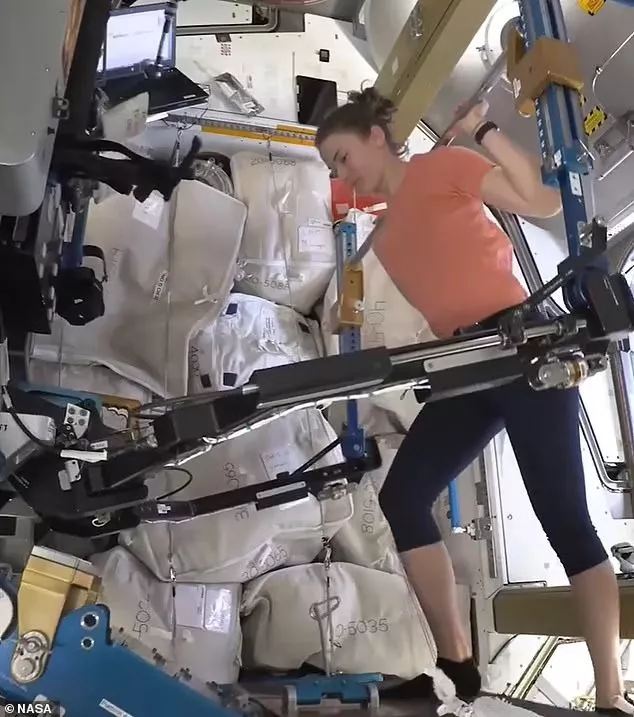


The ISS has three main pieces of exercise equipment for the astronauts to use which are located in the Tranquility module.
Astronauts can either choose to use an exercise bike called CEVIS, a treadmill called T2, or a weight-lifting system called ARED.
In the absence of gravity, the machines use a combination of pistons, flywheels, and elastic bands to simulate the force of an astronaut's weight.
During their time on the ISS, Williams and Wilmore, have even been taking part in weightless Olympics-inspired workouts in order to stay occupied and stay positive amid uncertainty.
















Comments