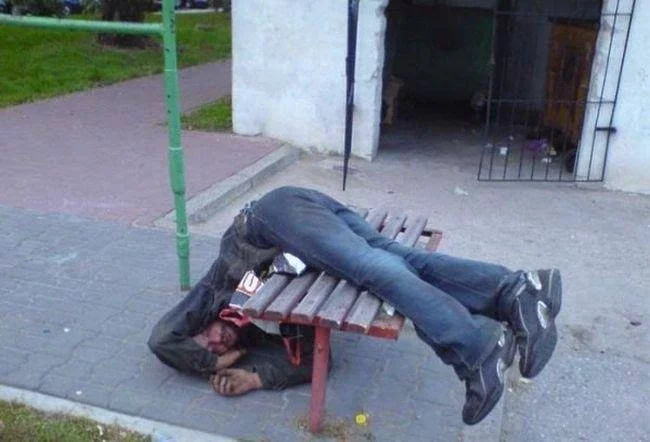


Drunk people are individuals who have consumed an excessive amount of alcohol to the point where their physical and mental abilities are impaired. Alcohol is a depressant that affects the central nervous system, leading to a range of behavioral changes that can be both amusing and dangerous.
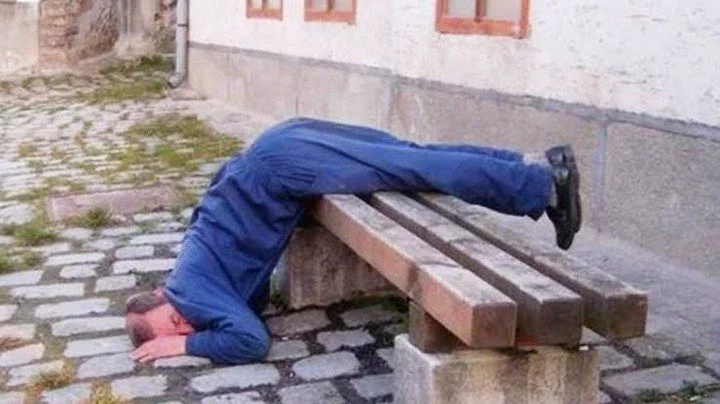

When people drink excessively, their inhibitions are lowered, and they may engage in behavior that they would not typically do when sober. They may become more talkative, outgoing, and confident, but at the same time, they may become more aggressive, violent, or depressed. Drunk people may also have trouble with coordination and balance, leading to stumbling and falling.
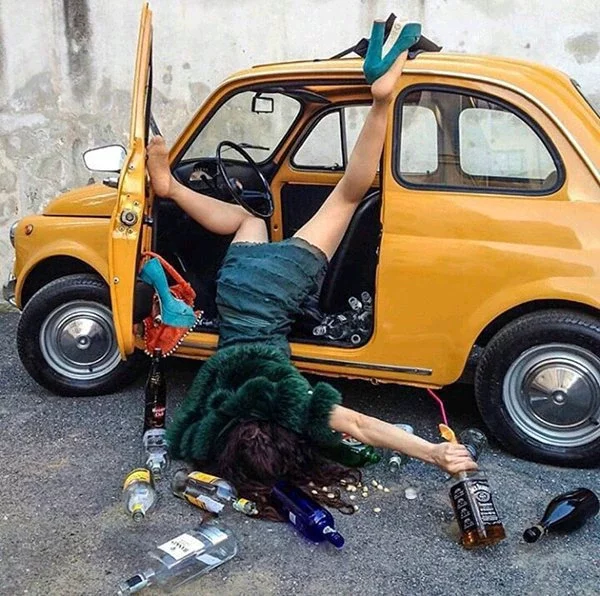

One of the most significant risks associated with drunk people is impaired judgment. They may make decisions that are unsafe or even life-threatening, such as driving while under the influence, operating heavy machinery, or engaging in risky sexual behavior. This impaired judgment can also lead to accidents, falls, and injuries.
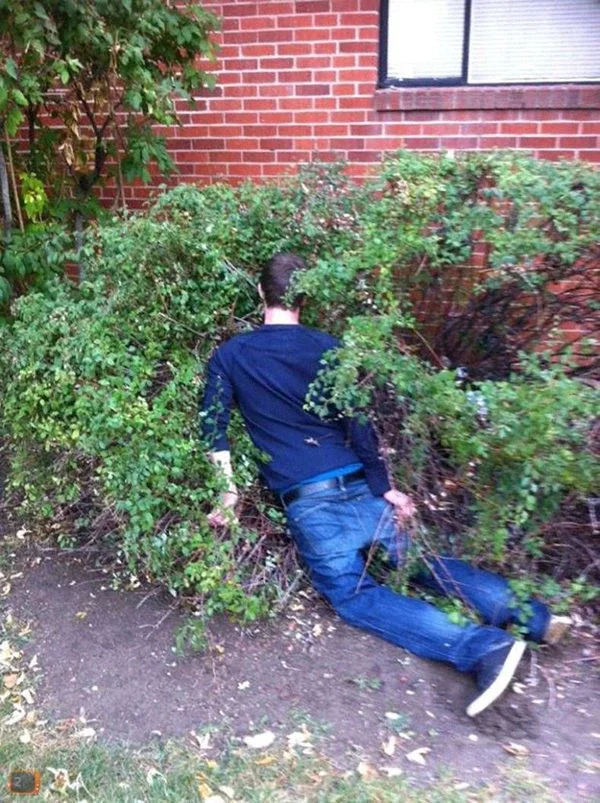

Another risk associated with drunk people is alcohol poisoning. When someone drinks too much alcohol too quickly, their body may not be able to process it all, leading to alcohol poisoning. Symptoms of alcohol poisoning include confusion, vomiting, seizures, and unconsciousness. In severe cases, alcohol poisoning can be fatal.

While it can be amusing to watch drunk people stumbling around or saying funny things, it is important to remember that alcohol abuse is a serious problem that can have severe consequences. Drinking in moderation is generally safe, but excessive drinking can lead to physical and mental health problems, relationship issues, and legal problems.

.
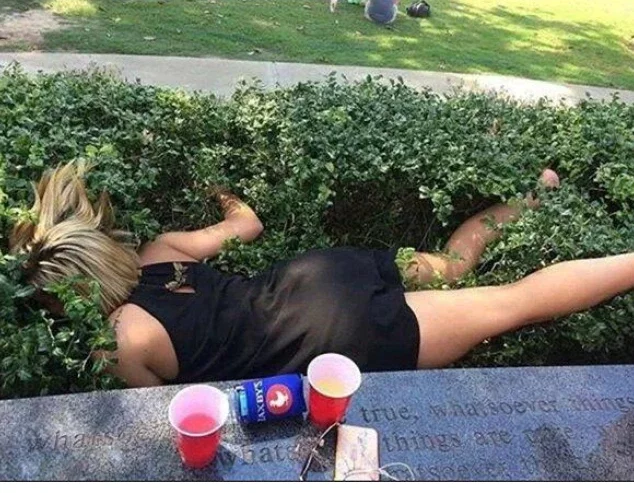



Overall, drunk people are individuals who have consumed an excessive amount of alcohol, leading to impaired physical and mental abilities, impaired judgment, and an increased risk of accidents, injuries, and alcohol poisoning. While it may be amusing to watch drunk people in some situations, it is important to remember that alcohol abuse is a serious problem that requires education, prevention, and treatment.














Comments