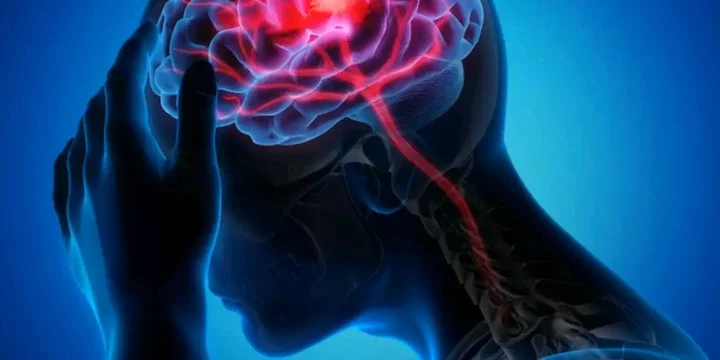
A stroke necessitates immediate medical intervention to mitigate damage to the affected area of the brain and prevent further complications.
The impact of a stroke depends on several factors, including the duration the brain is deprived of adequate oxygen and the specific region of the brain affected.
Strokes can result in a range of physical and cognitive impairments, making it a condition with significant consequences.
Some possible complications include:
Muscle Weakness or Paralysis: Strokes can lead to a loss of muscle control or mobility on one side of the body, which can manifest as complete paralysis or difficulty moving specific muscle groups.
Speech and Swallowing Difficulties:
Impaired control of mouth and throat muscles can result in difficulty speaking clearly, swallowing, or eating.
Cognitive Impairments: Some individuals may experience mental decline following a stroke, affecting their ability to think, reason, make decisions, or process thoughts effectively.
Emotional Changes: Stroke survivors may encounter mood swings, emotional instability, or even depression.
Sensory Changes: Individuals may lose feeling or experience unusual sensations in parts of their bodies affected by the stroke. Understanding the factors contributing to the risk of stroke can aid in its prevention.
Here, we discuss four elements that can increase the risk of stroke:
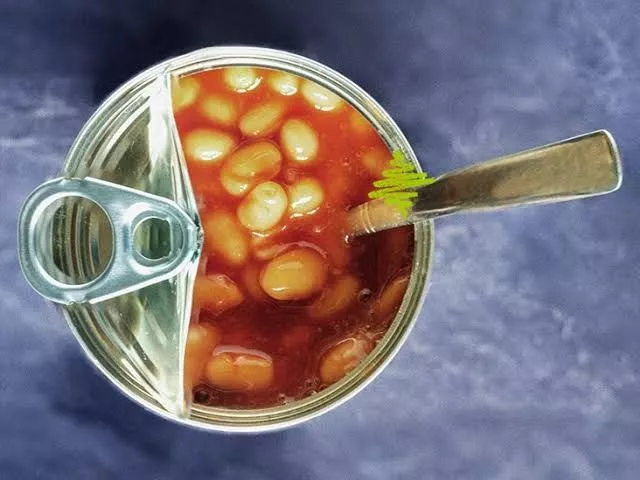
High Sodium Soups: Canned soups often contain elevated sodium levels to enhance flavor. High sodium intake is a significant risk factor for hypertension, a leading cause of stroke.
Research suggests that individuals consuming over 4,000 mg of sodium daily face double the risk of stroke compared to those consuming less than 2,000 mg.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: While light to moderate alcohol consumption might lower the risk of ischemic stroke, heavy alcohol use can increase the risk of all major stroke types.
Heavy alcohol consumption can lead to heart rate acceleration, blood vessel constriction, and weakening of brain blood vessels, contributing to strokes.
Processed Meats: Meats like pastrami, hot dogs, bacon, and smoked turkey are both high in sodium and contain added preservatives. High sodium and nitrate/ nitrite additives can harm blood vessels, increasing the risk of stroke and other health issues.
Red Meat Consumption: Regular
consumption of red meat has been linked to a higher stroke risk. Researchers found that people who consume less than one-third of a serving of red meat daily have a 28% lower risk of stroke compared to those who eat multiple servings daily.
Conversely, opting for alternative sources of protein like chicken, turkey, fish, or nuts can help reduce the likelihood of stroke.
Reducing sodium intake and consuming a balanced diet that minimizes processed and red meats can play a crucial role in stroke prevention.
Conversely, opting for alternative sources of protein like chicken, turkey, fish, or nuts can help reduce the likelihood of stroke.
Reducing sodium intake and consuming a balanced diet that minimizes processed and red meats can play a crucial role in stroke prevention.
It's important to note that stroke is a medical emergency, and recognizing its symptoms, such as sudden weakness or numbness, trouble speaking or understanding, and severe headaches, is vital for prompt medical intervention.













Comments