The ability to grow a full, thick beard is often associated with masculinity and can be a source of pride for many men. However, not all men are able to achieve the desired beard growth due to a variety of factors. While genetics plays a significant role in determining beard growth patterns, there are medical factors that can also influence the ability to grow a beard. In this article which is in accordance to healthline, we will explore the medical problems that can hinder beard growth in men, shedding light on the underlying causes and potential solutions.
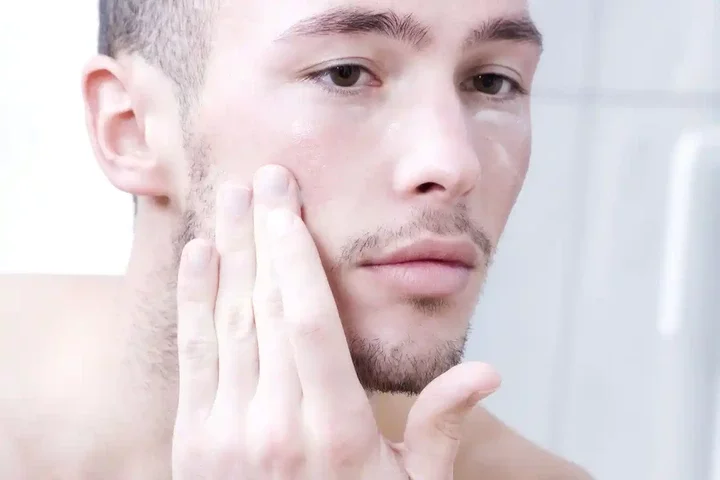

The Science of Beard Growth
Before delving into medical factors, it's important to understand the natural process of beard growth. Beard growth is primarily regulated by hormones, particularly testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). These hormones play a crucial role in the development of facial hair during puberty and its subsequent growth. The sensitivity of hair follicles to these hormones, along with genetic factors, determines the density, texture, and growth rate of facial hair.
Medical Problems that Can Hinder Beard Growth:
Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, affecting beard growth. Conditions such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, which involve an underactive or overactive thyroid gland, respectively, can impact hormone levels. Testosterone and DHT are crucial for beard growth, and any alterations in their levels can lead to sparse or slow beard growth.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that primarily affects women but can also have effects on men. Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) in men with PCOS can lead to various symptoms, including unwanted hair growth in certain areas and reduced beard growth in others.
Cushing's Syndrome:
Cushing's syndrome is characterized by excessive levels of cortisol, a stress hormone. High cortisol levels can disrupt the normal balance of hormones, including those involved in hair growth. As a result, beard growth may be compromised.
Genetic Predisposition:
Genetic factors are a major determinant of beard growth. Some men may simply have a genetic predisposition for limited facial hair growth due to their family history. Genes play a significant role in determining the sensitivity of hair follicles to hormones, which affects the pattern and density of beard growth.
Alopecia Areata:
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss in various areas of the body, including the beard area. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, resulting in hair loss or thinning.
Hypopituitarism:
Hypopituitarism is a condition where the pituitary gland does not produce adequate levels of hormones. Since the pituitary gland is responsible for regulating the release of various hormones, including those that influence hair growth, inadequate hormone production can impact beard growth.
Nutritional Deficiencies:
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly deficiencies in vitamins and minerals like biotin, zinc, and vitamin D, can affect the health of hair follicles. A lack of these nutrients can lead to brittle, thin hair that struggles to grow.
Chronic Illnesses and Medications:
Certain chronic illnesses and medications used to manage them can affect beard growth. Chronic stress, for example, can disrupt hormonal balance and impede hair growth. Additionally, medications like chemotherapy drugs may lead to temporary hair loss, including facial hair.
Skin Conditions:
Skin conditions that affect the face can hinder beard growth by affecting the hair follicles. Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or fungal infections can damage hair follicles and lead to hair loss in the beard area.
Androgenetic Alopecia:
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male-pattern baldness, can also impact beard growth. While it primarily affects the scalp, it can lead to reduced facial hair growth as well.
Solutions and Management:
Hormonal Treatments:
For individuals with hormonal imbalances, addressing the underlying hormonal issue can help improve beard growth. Hormone replacement therapy or other medications prescribed by a medical professional may be recommended to restore hormonal balance.
Lifestyle Changes:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact overall hair health, including beard growth. Getting regular exercise, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can contribute to healthier hair follicles.
Topical Treatments:
Some topical treatments, such as minoxidil, can stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. Minoxidil is commonly used to treat male-pattern baldness but can also be used to improve beard growth.
Consulting a Dermatologist:
If you suspect a medical condition is affecting your ability to grow a beard, consulting a dermatologist or an endocrinologist is advisable. These healthcare professionals can conduct thorough evaluations, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatments or interventions.
Nutritional Supplements:
If nutritional deficiencies are contributing to poor beard growth, supplements containing biotin, zinc, and other essential vitamins and minerals can be considered. However, it's important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation regimen.
Hair Transplantation:
In cases of severe beard hair loss, hair transplantation procedures can be an option. Hair follicles are extracted from other parts of the body and transplanted to the beard area, promoting new hair growth.
Managing Underlying Conditions:
Treating underlying medical conditions, such as alopecia areata or hypopituitarism, can have a positive impact on overall hair health and beard growth.








![These Two Beautiful UNILAG Students Died In An Hotel Fire [Photos ] These Two Beautiful UNILAG Students Died In An Hotel Fire [Photos ]](https://img.netnaija.com/hsi/aHR0cDovL3d3dy5uYWlqYWxvYWRlZC5jb20ubmcvd3AtY29udGVudC91cGxvYWRzLzIwMTcvMDgvMS0xMTQuanBn/images/1-114.jpg)


Comments