Diabetic nerve damage, also known as diabetic neuropathy, is a common complication of diabetes that affects the nerves throughout the body. Over time, persistently high blood sugar levels can damage the delicate nerve fibers, leading to a range of symptoms and potential health complications. Recognizing the early signs of diabetic nerve damage is crucial for prompt intervention and management. According to healthline, This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the early signs of diabetic nerve damage that should not be ignored, emphasizing the importance of early detection to prevent further health complications.
Tingling and Numbness:
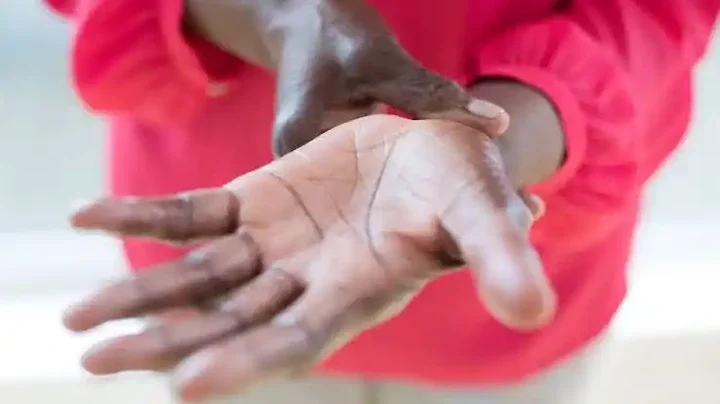

One of the earliest and most common signs of diabetic nerve damage is tingling and numbness, typically starting in the extremities. This sensation, known as peripheral neuropathy, often affects the toes, feet, fingers, and hands. The tingling may be accompanied by a feeling of pins and needles or a loss of sensation. Diabetic individuals experiencing persistent tingling or numbness should seek medical attention to prevent further nerve damage.
Loss of Sensation:
As diabetic nerve damage progresses, the loss of sensation can become more pronounced. Individuals may experience a reduced ability to feel touch, temperature, or pain in the affected areas. This can lead to difficulties in detecting injuries or wounds, increasing the risk of infection and delayed healing. Regular self-examinations and foot care routines are essential for diabetic patients to identify any changes in sensation and seek appropriate medical care.
Muscle Weakness:
Muscle weakness can occur as a result of nerve damage in individuals with diabetes. As the nerve signals to the muscles become compromised, weakness and difficulty in performing everyday activities can manifest. Tasks such as walking, grasping objects, or maintaining balance may become challenging. Diabetic individuals experiencing unexplained muscle weakness should consult their healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation.
Digestive Issues:
Autonomic neuropathy, a form of diabetic nerve damage that affects the autonomic nervous system, can lead to digestive problems. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea. Diabetic individuals experiencing persistent or recurrent gastrointestinal issues should not dismiss these symptoms as they may indicate underlying nerve damage and should seek medical evaluation.
Sexual Dysfunction:
Diabetic nerve damage can affect the nerves controlling sexual function, leading to various forms of sexual dysfunction. Both men and women may experience decreased libido, erectile dysfunction in men, vaginal dryness in women, and difficulties in achieving orgasm. These changes can significantly impact the quality of life and relationships. Diabetic individuals should address any sexual health concerns with their healthcare provider for appropriate management and support.
Bladder Problems:
Nerve damage can disrupt the normal functioning of the bladder, resulting in urinary problems. Diabetic individuals may experience urinary incontinence, a frequent need to urinate, or difficulty emptying the bladder completely. These symptoms can be indicative of diabetic nerve damage affecting the nerves controlling bladder function. Seeking medical guidance can help manage these issues and prevent complications such as urinary tract infections.
Vision Changes:
Diabetic nerve damage can affect the nerves in the eyes, leading to vision changes. Individuals may experience blurred vision, difficulty focusing, or fluctuating vision. This may be a sign of diabetic retinopathy, a condition caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Prompt eye examinations by an ophthalmologist are crucial for early detection and treatment of any eye-related complications.
Balance and Coordination Problems:
Peripheral neuropathy can affect the nerves responsible for balance and coordination, leading to difficulties in walking and maintaining stability. Diabetic individuals may experience unsteadiness, a tendency to stumble or fall, and altered gait patterns. These symptoms should not be ignored, as they increase the risk of injuries and fractures. Seeking medical evaluation and engaging in appropriate physical therapy can help improve balance and reduce the risk of falls.
Recognizing the early signs of diabetic nerve damage is essential for timely intervention and prevention of further complications. Diabetic individuals should be vigilant and attentive to any changes in sensation, muscle strength, digestive function, sexual health, bladder control, vision, or balance. Seeking medical evaluation and working closely with healthcare professionals can help manage diabetic neuropathy effectively, prevent progression, and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Alongside maintaining good glycemic control, lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and regular foot care, are vital in minimizing the impact of diabetic nerve damage and preserving overall health and well-being.













Comments