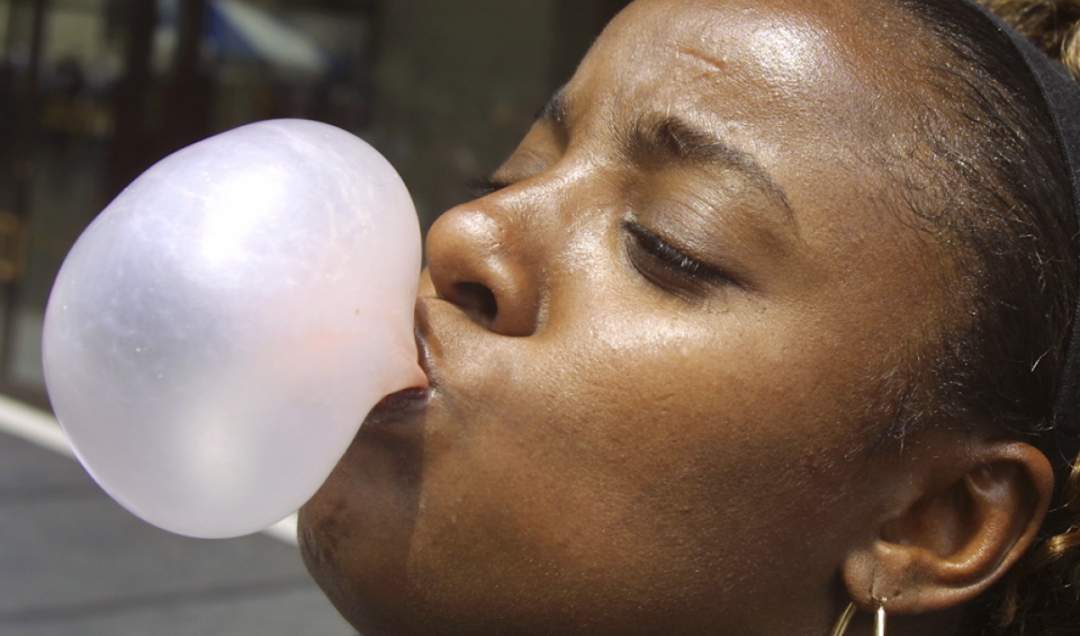

People have been chewing gum in various forms for thousands of years. Original gums were made from the sap of trees. However, most modern chewing gums are made from synthetic rubbers.
Because they are synthetic, they have some negative effects. Below are some of the effects of chewing gum:
Gastrointestinal Problem
Chewing gum causes you to swallow excess air, which can cause abdominal pain and bloating. Also, when you chew gum, you send a signal to your body that it's time to digest food. But without any food to digest, you end up with an overproduction of stomach acid. This can also cause bloating.
Tooth Damage
When you chew sugary gum, you open your tooth to tooth decay. Even if you're chewing sugar-free gum, you can cause tooth damage. Sugar-free gum often contains acidic flavourings that can lead to dental erosion, which can, over time, dissolve your teeth.
It Can Trigger TMJ (Temporomandibular Joint Disorder):
Chewing gum can cause a jaw muscle imbalance if you chew on one side more than the other. It can also cause a painful and chronic condition known as TMJ or Temporomandibular Joint Disorder.
Headache
When chewing, 8 facial muscles are involved. Unnecessary chewing can create chronic tightness in two of these muscles, located close to your temples which can lead to chronic, intermittent headaches.
Masks bad breath
Chewing gum does not take away bad breath, rather, it masks bad breath. Bad breath is symptom of digestive problems or excessive tooth decay. So, if you do not treat it, it won't go away.
Diarrhea
The sugar alcohols used to sweeten sugar-free gum have a laxative effect when used in large amounts. This means that chewing lots of sugar-free gum could cause digestive distress and diarrhea. Additionally, all sugar alcohols can cause digestive problems for people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).















Comments